The quality of physical habitat for juvenile salmonids is defined according to specifications outlined by the Water Quality Parameter and Habitat Productivity Technical Group. Habitat quality is assessed in terms of temperature, salinity and dissolved oxygen thresholds, with four categories defined for each variable.
Temperature:
| \(14-18^\circ\text{C}\) |
\(< 14^\circ\text{C}\) or \(18-21^\circ\text{C}\)
|
\(21-25^\circ\text{C}\) |
\(> 25^\circ\text{C}\) |
Dissolved Oxygen:
| \(> 6 \text{ mg/L}\) |
\(4-6 \text{ mg/L}\) |
\(3-4 \text{ mg/L}\) |
\(< 3 \text{ mg/L}\) |
Salinity:
| \(< 10 \text{ ppt}\) |
\(10-15 \text{ ppt}\) |
\(15-28 \text{ ppt}\) |
\(> 28 \text{ ppt}\) |
| Low energy demand |
negligible energy demand |
high energy demand (freshwater-acclimated) |
unsuitable (freshwater acclimated) |
|
|
low energy demand (saltwater-aclimated) |
moderate energy demand (saltwater-aclimated) |
Overall Habitat
To assess the overall habitat quality of a region, the individual ratings are into the 9 categories defined below.
| Optimal |
optimal or positive growth (T); minimal impairment (DO); Low or negligible energy demand (S) |
| Growth limited |
no/negative growth (T); minimal impairment (DO); Low or negligible energy demand (S) |
| Impaired |
optimal or positive growth (T); some or severe impairment (DO); Low or negligible energy demand (S) |
| Energy demanding |
optimal or positive growth (T); minimal impairment (DO); moderate or high energy demand (S)
|
| Growth limited, impaired |
no/negative growth (T); some or severe impairment (DO); Low or negligible energy demand (S) |
| Growth limited, energy demanding |
no/negative growth (T); minimal impairment (DO); moderate or high energy demand (S)
|
| impaired, energy demanding |
optimal or positive growth (T); some or severe impairment (DO); moderate or high energy demand (S)
|
| Growth limited, impaired, energy demanding |
no/negative growth (T); some or severe impairment (DO); moderate or high energy demand (S)
|
| Unsuitable |
any one of: unsuitable (T); unsuitable (S); unsuitable (DO)
|
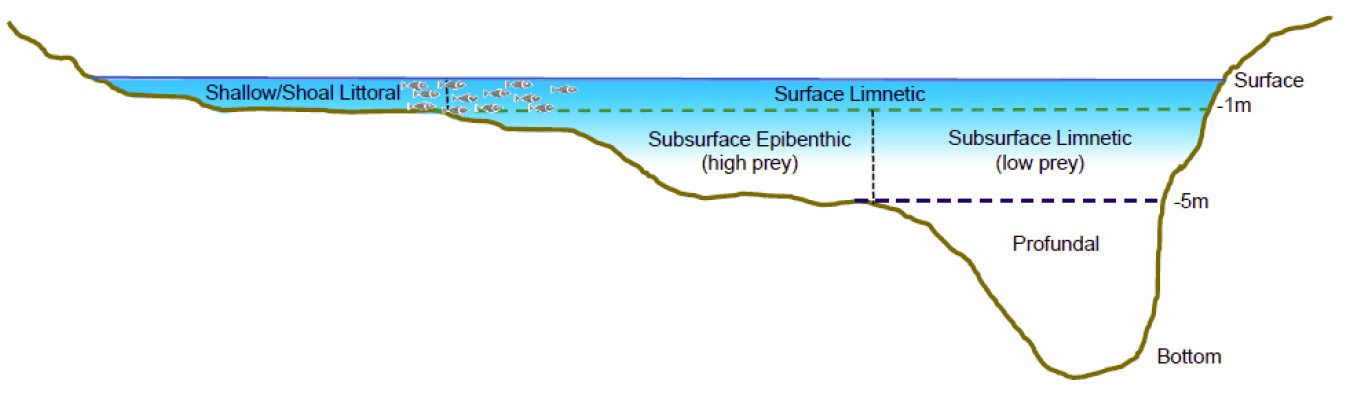
Depth Zone Definitions
Habitat quality can also be assessed based on water depth, which has important implications for foraging, shelter and predation risk. The Water Quality Parameter and Habitat Productivity Technical Group has defined a separate set of habitat categories that assess habitat in terms of water depth.
| Littoral (Shallow/shoal) |
High prey availability, high avian predation risk, low aquatic predation risk |
\(depth < 1\text{m}\) and \(\max{(depth)} < 1\text{m}\)
|
| Surface Limnetic |
Low prey availability, high avian predation risk, high aquatic predation risk |
\(depth < 1\text{m}\) and \(\max{(depth)} \geq 1\text{m}\)
|
| Epibenthic |
High prey availability, low avian predation risk, moderate aquatic predation risk |
\(1\text{m} \leq depth \leq 5\text{m}\) and \(\max{(depth)} \leq 5\)
|
| Subsurface Limnetic |
Low prey availability, low avian predation risk, moderate aquatic predation risk |
\(1\text{m} \leq depth \leq 5\text{m}\) and \(\max{(depth)} > 5\)
|
| Profundal |
Low prey availability, no predation risk |
\(depth > 5\text{m}\) |